Guide: What is Machine Learning Algorithms and How They Work

At its core, a machine learning algorithm isn't just a piece of code. It's a method—a set of rules and statistical techniques—that lets a computer learn directly from data. Instead of a developer writing explicit, step-by-step instructions for every possible scenario, the algorithm figures out the patterns on its own.
This is the fundamental shift: we’re teaching systems how to learn, not just what to do.
Decoding the Engines of Modern AI
Think of an algorithm as a chef's recipe. The recipe gives you the framework, but the final dish depends entirely on the ingredients (the data) you use. A novice chef might follow the recipe to the letter, but an expert learns by tasting and adjusting based on the quality of those ingredients.
Machine learning algorithms do the same thing. They take in data, process it according to their "recipe," and produce an output, like a prediction or a classification. The more data they process, the more they refine their approach, getting better and better at the task. This learning loop is what makes them so powerful.
These are the engines driving everything from your Netflix recommendations to the sophisticated systems that flag fraudulent credit card transactions. Each algorithm is designed to solve a specific kind of problem by uncovering the hidden relationships within a dataset.
The Role of Data and Models
To really get what an algorithm is, you have to see how it connects with data and models. The algorithm is the process that chews through the data to create a model. This model is the final, tangible output of all that training—a compact, usable representation of everything the algorithm learned.
For example, an algorithm built to spot spam emails will analyze thousands of messages, both spam and legitimate. It learns to associate certain words, sender patterns, or phrasing with spam. The final output is a spam filter model that can accurately classify brand-new emails it has never seen before.
"The number of parameters is usually not the best way to measure the generalization capabilities of a learning method." This insight is key—it’s not just about complexity. A great algorithm learns the right patterns without getting sidetracked by noise in the data.
Why This Matters for Business Leaders
For business leaders and event planners, you don't need to master the complex math behind these algorithms. What's crucial is understanding their capability. Knowing how they work opens the door to strategic innovation and helps you ask the right questions.
As expert speakers like Dr. Ava Chen often explain in her keynotes, this foundational knowledge empowers teams to spot opportunities where AI can create real, measurable value.
To provide a quick reference, here’s a simple breakdown of the core components in a machine learning system.
Core Components of Machine Learning at a Glance
| Component | Role and Analogy | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Data | The ingredients. This is the raw material the algorithm learns from. | A database of customer purchase histories. |
| Algorithm | The recipe. This is the process that finds patterns in the data. | A classification algorithm like a Decision Tree. |
| Model | The finished dish. This is the output that can make predictions on new data. | A predictive model that suggests which products a customer is likely to buy next. |
This table neatly captures the journey from raw information to actionable intelligence, which is the heart of machine learning. The rest of this guide will dive into the different types of algorithms and show how they solve distinct problems across various industries.
The Three Pillars of Machine Learning
Machine learning isn't a single, monolithic thing. It's a huge field built on three core approaches, or "pillars." Getting a handle on these categories is the first step to understanding how different algorithms tackle different problems. Each pillar represents a unique style of learning, shaped by the kind of data you have and what you’re trying to achieve.
Think of them less like dense computational theories and more like intuitive learning strategies. Once you grasp them, you'll have a mental map to navigate the entire AI landscape.
Let's break down each one.
Supervised Learning: Teaching with an Answer Key
Supervised learning is the most common and straightforward type of machine learning. The big idea is simple: the algorithm learns from data that already has the "right answers" attached. It's like a student cramming for a test with flashcards—each card has a question on the front and the correct answer on the back.
The algorithm is "supervised" because a human "teacher" has already provided the correct outcomes. Its job is to figure out the hidden patterns that connect the inputs to those known outputs. After crunching through thousands of these labeled examples, the model gets good enough to predict answers for brand-new data it's never seen.
This approach is a workhorse for two main kinds of tasks:
- Classification: This is all about sorting things into neat categories. A classic example is your email spam filter. It learns from thousands of emails you’ve marked as "spam" or "not spam" to automatically classify new messages.
- Regression: This is used for predicting a specific number. Think of a real estate app predicting a house's price based on its square footage, number of bedrooms, and location—all learned from a huge dataset of past home sales.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Patterns on Its Own
So, what happens when you have a mountain of data but no labels? That's where unsupervised learning comes in. This type of algorithm is like an explorer charting unknown territory without a map or a guide. Its goal is to dive into the data and discover hidden structures, groupings, or weird outliers all by itself.
Instead of predicting a known answer, unsupervised learning is about understanding the data’s inherent structure. It's incredibly powerful for finding patterns that no human would ever spot.
Common uses include:
- Clustering: This involves grouping similar data points together. A marketing team might use this to segment customers into different buckets based on their buying habits, paving the way for hyper-targeted campaigns.
- Association: This is about discovering rules that describe big chunks of your data. It’s the magic behind the "customers who bought this also bought..." feature on Amazon.
For a deeper dive into how these two fundamental pillars stack up, check out our guide on supervised learning vs unsupervised learning.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning Through Trial and Error
The third pillar, reinforcement learning, plays by a totally different set of rules. It’s a lot like how you’d train a dog to do a new trick. You don't show it a bunch of examples; you reward it for getting things right and offer no reward (or even a penalty) for getting them wrong. Over time, the dog figures out which actions lead to a treat.
A reinforcement learning algorithm, often called an "agent," learns by doing. It interacts with an environment, tries different actions, sees what happens, and gets rewards or penalties. The agent's only goal is to rack up the biggest possible reward over time. This trial-and-error process makes it perfect for complex, dynamic problems where the best path forward isn't obvious from the start.
This is the approach behind some of AI's most stunning achievements, from mastering ridiculously complex games like Go to training robotic arms to perform delicate tasks with superhuman precision. It’s the go-to for any problem that requires making a sequence of smart decisions.
The rise of deep learning and neural networks has supercharged all three pillars. Back in the 2010s, image recognition took a massive leap when the AlexNet neural network cut the error rate on the ImageNet dataset down to 15.3%—a huge jump from the typical 26% of older models. A few years later, in 2014, Facebook’s DeepFace algorithm hit 97.35% accuracy in face recognition, basically matching human ability. These breakthroughs were all fueled by massive datasets and way more powerful computers. You can learn more about the history of these advancements to see just how far we've come.
A Practical Look at Key Algorithms
Knowing the three main branches of machine learning is a great start, but the real magic happens inside the specific algorithms—the engines that actually do the work. Let's move from high-level concepts to the practical tools you'll encounter day-to-day. We'll skip the heavy math and focus on the intuitive logic behind how they solve problems.
This quick tour will help you connect the dots between an algorithm's name and its power to solve real-world business challenges.
The diagram below gives you a clean visual breakdown of how these algorithms fit into the bigger picture.
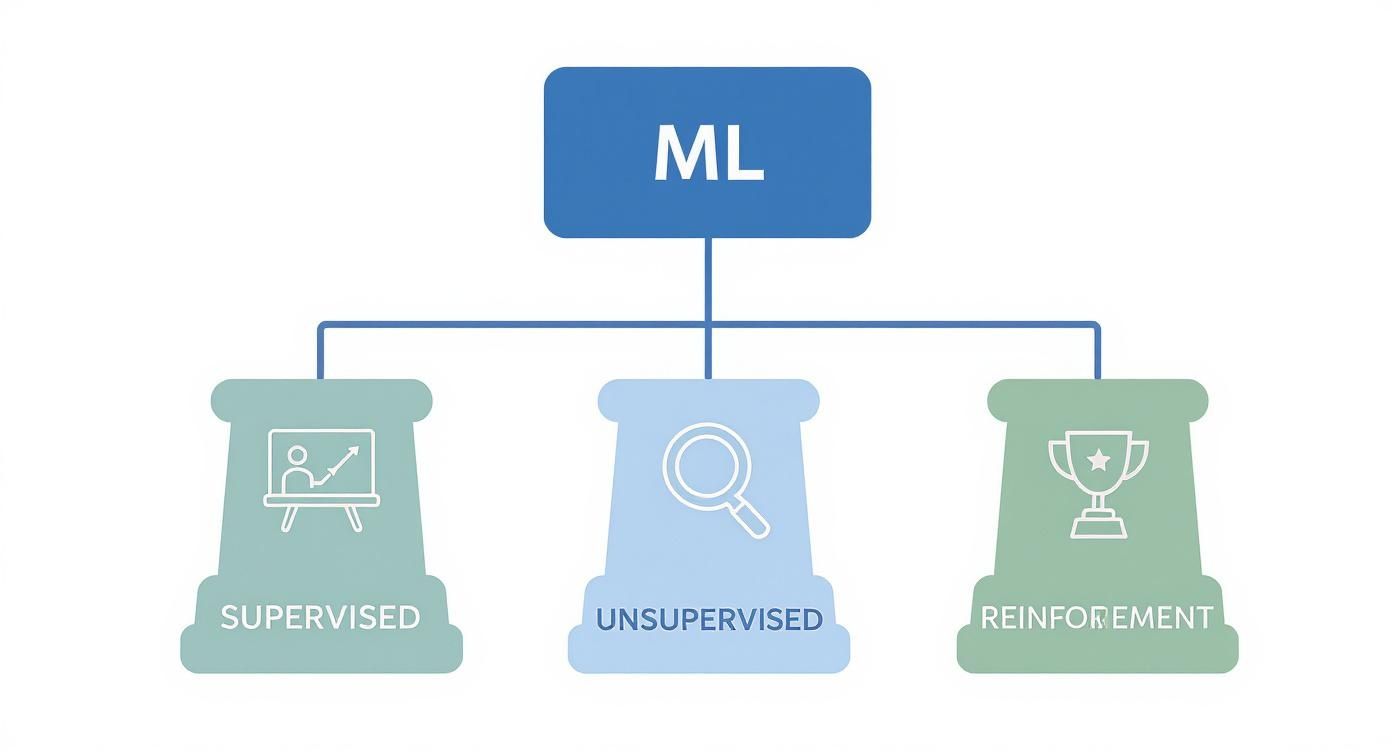
As you can see, Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning are the foundational pillars. Now, let’s see what they look like in action.
Linear Regression: The Predictive Workhorse
Linear Regression is the first stop for many people entering the world of machine learning, and for good reason. It’s a straightforward but powerful tool from the supervised learning family, built to predict a continuous number—think price, temperature, or sales volume.
Imagine you're trying to figure out a house's price. You've got data on past sales: square footage, number of bedrooms, location, and so on. Linear Regression draws the best possible straight line to show the relationship between those features and the final selling price.
Once that line is drawn, you can feed it the details of a new house, and it will give you a solid price estimate. It's the ultimate algorithm for answering questions that start with "how much?" or "how many?"
Decision Trees: Making Choices Clear
Also a supervised learning favorite, the Decision Tree operates just like you do when making a tough choice—by breaking it down into a series of smaller, simpler questions. It creates a flowchart-like model to predict an outcome, making its logic incredibly easy to follow.
Think of it as a game of "20 Questions." The algorithm asks a series of yes-or-no questions to narrow down the possibilities and land on a conclusion. A bank, for instance, could use a Decision Tree to screen loan applications.
- Is the applicant's credit score over 700?
- Is their annual income more than $50,000?
- Have they been at their current job for over two years?
By following these branches, the model classifies an applicant as "low risk" or "high risk." Their transparency makes them a go-to in fields like finance and healthcare, where being able to explain why a decision was made is non-negotiable.
The real value of algorithms like Decision Trees lies in their clarity. They don't just give you an answer; they show you exactly how they reached it, building trust in the model's output.
K-Means Clustering: Finding Natural Groups
Let's switch gears to unsupervised learning with K-Means Clustering. This is your best friend when you’re staring at a mountain of data with no labels and need to find the natural, hidden groupings within it.
The "K" simply stands for the number of clusters you tell the algorithm to find. It then works iteratively, assigning each data point to the nearest cluster's center (called a "centroid") and then recalculating the centers until the groups become stable.
A classic use case is customer segmentation. An online retailer could use K-Means on its customer data and discover distinct clusters like "budget shoppers," "brand loyalists," and "seasonal buyers." Suddenly, they have the insights needed to create laser-focused marketing campaigns for each group.
Support Vector Machines: The Precision Classifier
Back in the supervised learning camp, Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are heavy-hitters known for their incredible accuracy in classification tasks, especially when the data is complex. An SVM doesn't just draw a line to separate groups; it finds the best possible line.
Picture a chart with data points for two groups, like cancerous vs. non-cancerous cells. An SVM's goal is to draw a boundary (a "hyperplane") between them that is as wide as possible.
This "maximum margin" approach makes the model robust. It’s less likely to make a mistake when new data points fall close to the boundary. You'll find SVMs in bioinformatics, text analysis, and image recognition—anywhere precision is absolutely critical.
To help you keep these tools straight, here’s a quick comparison of the algorithms we’ve just covered.
Common Machine Learning Algorithms Compared
This table offers a snapshot of each algorithm, highlighting its type, primary use, and a concrete example to help you see where it fits best.
| Algorithm | Learning Type | Best For | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Regression | Supervised | Predicting continuous numerical values. | Forecasting quarterly sales based on marketing spend and seasonality. |
| Decision Trees | Supervised | Making transparent, rule-based classifications. | A healthcare system identifying high-risk patients based on their medical history. |
| K-Means Clustering | Unsupervised | Discovering inherent groups in unlabeled data. | Grouping news articles by topic without any prior categorization. |
| Support Vector Machine | Supervised | High-accuracy classification with clear margins. | Identifying handwritten digits on a postal envelope for automated sorting. |
Each of these algorithms offers a unique way to turn raw data into valuable insights. Choosing the right one depends entirely on the question you're trying to answer and the nature of the data you have.
Understanding Neural Networks and Reinforcement Learning
While algorithms like Linear Regression and Decision Trees are incredibly useful, some problems are just too messy and dynamic for them to handle. This is where we get into the really exciting stuff—two areas that are behind many of the AI breakthroughs you see in the news today: Neural Networks and Reinforcement Learning.
These advanced methods are designed for the kind of complexity that stumps simpler models, paving the way for things like understanding human language and making autonomous decisions.
Neural Networks: The Brain of Deep Learning
At the center of the deep learning boom is the neural network, an algorithm inspired by the tangled web of neurons in the human brain. Instead of following a straight line or a rigid set of if-then rules, a neural network is built from interconnected layers of nodes, or "neurons."
Each neuron takes in information, chews on it, and passes its conclusion to the next layer. The first layer might look at the raw pixels of an image. The next layer might recognize simple edges and curves from those pixels. The layer after that could combine those edges into shapes like eyes and noses, until the final layer confidently declares, "That's a face."
This layered, hierarchical structure is the magic ingredient. It allows neural networks to learn incredibly subtle patterns from mountains of data, which is what machine learning algorithms look like when they're built for massive complexity. They are the engine behind:
- Image Recognition: Spotting objects, people, and scenes in photos with stunning accuracy.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Making tools like Google Translate, chatbots, and sentiment analysis possible.
- Generative AI: Creating entirely new text, images, and code, like the models behind ChatGPT.
The key takeaway here is that neural networks thrive on nuance and context. They uncover the deep, intricate relationships within data that other algorithms just can’t see, making them the champions of unstructured data like text and images.
Making these complex systems work for your business strategy is a whole other challenge. This is precisely where an expert like Dr. Kenji Tanaka, one of the leading voices on our speaker roster, provides immense value. Dr. Tanaka has a rare talent for translating the power of deep learning into practical business applications, helping executive teams turn these advanced tools into a real competitive edge.
Reinforcement Learning: Mastering Skills Through Trial and Error
Unlike supervised learning, which relies on a perfectly labeled dataset, Reinforcement Learning (RL) works a lot like training a puppy. The algorithm, or "agent," learns by interacting with an environment and trying to achieve a goal. You reward good behavior and simply don't reward bad behavior.
The agent takes an action, sees what happens, and gets a reward (a treat!) or a penalty (nothing). After millions of these trial-and-error cycles, it builds a "policy"—a gut instinct for which actions will lead to the biggest long-term reward. This approach is perfect for dynamic situations where the rules of the game aren't fully known. For a deeper dive, check out our dedicated guide on what is reinforcement learning.
This constant learning from experience makes RL the ideal solution for complex problems that involve a sequence of decisions.
Where RL and Neural Networks Shine
Reinforcement learning is the technology behind some of AI’s most mind-blowing achievements. The agent figures out the best strategy all on its own, without a human programmer telling it the "right" move at every turn.
Here’s where you can see RL in action:
- Robotics: A factory robot learns to pick up and place delicate objects by repeatedly trying, failing, and refining its grip.
- Gaming: AI agents taught themselves to beat the world's best players in ridiculously complex games like Go and Dota 2 by playing against themselves for millions of hours.
- Resource Management: A system learns to optimize the cooling in a data center or manage city traffic lights by adapting to real-time conditions.
Often, neural networks and reinforcement learning team up in a powerful combination known as Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL). In this setup, a deep neural network serves as the agent's "brain," allowing it to process complicated inputs (like the raw pixels from a video game) and make smart, strategic decisions. This partnership is what allowed an AI to master Atari games just by looking at the screen—a true landmark in the field.
How Algorithms Are Transforming Industries
The theory behind what machine learning algorithms are is interesting, but their real power snaps into focus when you see them at work. These aren't just abstract ideas stuck in a research lab; they're practical tools actively reshaping entire sectors. From hospitals to Wall Street, algorithms are tackling thorny problems and creating tangible value.
This real-world impact is a central theme our industry-veteran speakers love to dig into. They bring stories straight from the front lines, showing how a single, well-chosen algorithm can become a company’s most powerful asset. The results are impossible to ignore: greater efficiency, genuine innovation, and a serious competitive edge.
Healthcare From Reactive to Predictive
In healthcare, machine learning is flipping the script from treatment to prevention. Institutions are now using classification algorithms, like Support Vector Machines (SVMs), to comb through patient data—everything from lab results to genetic markers—and predict the likelihood of disease long before symptoms ever show up.
This predictive power is a complete game-changer. Imagine algorithms that can scan medical images like MRIs with superhuman precision, flagging the earliest signs of a tumor that a person might miss. This leads to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and, most importantly, better outcomes for patients.
Finance Fortifying Against Fraud
The financial world runs on speed and trust, which makes it a perfect playground for machine learning. Banks and fintech startups now deploy incredibly sophisticated algorithms to spot fraudulent transactions the second they happen. These systems churn through millions of transactions, instantly flagging weird patterns that scream "theft."
- Behavioral Analysis: An algorithm learns your unique spending fingerprint—where you shop, what you buy, and when.
- Anomaly Detection: If a charge suddenly pops up from another country or for an unusually large amount, the system flags it immediately.
- Reduced False Positives: Today’s algorithms are so sharp they minimize those frustrating moments when your own legitimate purchases get declined.
This nonstop digital watchdog protects consumers and saves financial institutions billions of dollars every year. For a deeper dive, check out our comprehensive list of AI use cases by industry.
E-commerce and Personalization
E-commerce giants like Amazon didn't just get lucky; they built their empires on powerful recommendation engines fueled by unsupervised and supervised learning algorithms. These systems track your browsing history, what you've bought before, and even what people like you have purchased to create a shopping experience that feels like it was built just for you.
It's not just about showing you more stuff; it's about showing you the right stuff at the right time. As these algorithms get smarter, their influence is being felt everywhere, even shaping how companies approach managing software development in the AI era. The payoff is huge: more engaged customers, higher sales, and a healthier bottom line.
Bring Machine Learning Clarity to Your Team
Getting a handle on what machine learning algorithms are is a great start. But the real magic happens when you start applying that knowledge. We've seen how these algorithms—from supervised to reinforcement learning—act as the engines that transform raw data into smart decisions, making a real impact in fields like healthcare, finance, and beyond.
But let's be honest, turning that potential into a genuine advantage for your organization takes more than just reading an article. It requires a clear, guided conversation led by someone who's been in the trenches.
Your Direct Connection to AI Experts
That’s where we come in. Speak About AI connects you with world-class machine learning experts who can demystify these complex topics for your team. Our roster is filled with top researchers, industry pioneers, and gifted communicators who know how to make AI accessible and, more importantly, actionable. To get there, an expert guide to knowledge management and artificial intelligence provides a fantastic framework for organizing your internal expertise first.
Whether you need an inspiring keynote to get the entire company on the same page or a hands-on workshop for your technical teams, our speakers deliver. They don't just throw concepts at the wall; they empower your people to innovate with confidence.
Our mission is to bridge the gap between abstract AI theory and tangible business outcomes, ensuring your team is not just informed, but also inspired to act.
Ready to bring this level of insight to your next event? Contact Speak About AI today, and we’ll help you find the perfect expert to educate and energize your team.
Your Top ML Algorithm Questions Answered
To wrap things up, let's tackle some of the most common questions that come up when people start working with machine learning. Think of this as the practical advice you need to move from theory to action.
Which Algorithm Is Best for My Business Problem?
This is the million-dollar question, and the honest answer is: there’s no single "best" one. The right algorithm is always the one that best fits your specific goal and, just as importantly, the data you actually have.
- Need to predict a number, like future sales or housing prices? Start with Linear Regression. It’s straightforward and a great baseline.
- Trying to sort things into buckets, like whether an email is spam or not? Decision Trees or Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are fantastic choices.
- Want to discover natural groupings in your customer base without any predefined labels? K-Means Clustering is your go-to for that kind of discovery.
The real skill is matching the algorithm's strengths to the business question you're asking. It’s a common stumbling block, which is why our expert speaker, Dr. Ava Chen, often runs workshops that help teams pinpoint the perfect algorithm for their unique challenges. It’s all about starting on the right foot.
How Much Data Do I Need to Train an Algorithm?
The answer really depends on the complexity of the job. A simple algorithm like Linear Regression can deliver solid results with a relatively small, clean dataset. But if you’re venturing into the world of deep learning and neural networks, you’ll need a massive amount of data—sometimes millions of examples—for the model to learn effectively.
But here’s a pro tip: the quality and relevance of your data almost always trump sheer quantity. A smaller set of clean, well-labeled data will get you much further than a massive, messy one.
Can an Algorithm Be Biased or Unfair?
Yes, absolutely. This is one of the most critical issues in AI today. An algorithm is only as good as the data it learns from. If your training data contains historical human biases—like gender or racial inequality in past hiring decisions—the model will not only learn those biases, it will often amplify them.
This isn’t just a technical problem; it’s an ethical one. It's a topic that speakers like Dr. Kenji Tanaka are dedicated to addressing. He specializes in helping organizations audit their systems, understand the risks of algorithmic bias, and build fairer, more responsible AI.
Navigating these nuances is what separates a successful AI project from a failed one. At Speak About AI, we connect you with the world's leading experts who provide the clarity and strategic guidance your team needs to get it right.
